Search engines started to appear in 1993 to allow people to find web content matching specific criteria (typically those containing a given word or phrase). They provide results typically as a list of references of those sites that match the search criteria. From around 1994 search engines started to index full text from pages but it wasn’t until 1998 when Google was launched that search engines started to get more intelligent on how they indexed web page content and presented this in search results. Google’s search tried to rank sites and pages based on how many other sites linked to them. Combined with the minimalist user interface and relevant search results they have become the most popular web search in the world.
Google is the top search engine in Argentina, Australia, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Denmark, France, Germany, India, Italy, Mexico, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, U.K., U.S. – source Nielsen//Netratings 6/05, based on total number of unique visitors.
The Neilsen//Netratings August ‘US Search share’ rankings state Google has 50.2% of US searches:
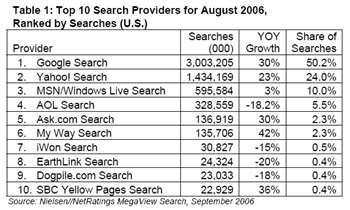
Taken from http://www.nielsen-netratings.com/pr/pr_060919.pdf
Search engines work by using automated programs called robots (other names include spiders, crawlers and bots) to traverse the web and follow hyperlinks to new and undiscovered web pages. During this ‘crawl’ they index content from pages and this is used to create the search results. Over time they re-visit pages to see if they have changed and also to check that they are still available and can be accessed.
